Why invest in Azerbaijan
Political and economic stability
- 2nd fastest growing economy among 179 countries in terms of GDP per capita growth in 2001-2010 (The Economist).
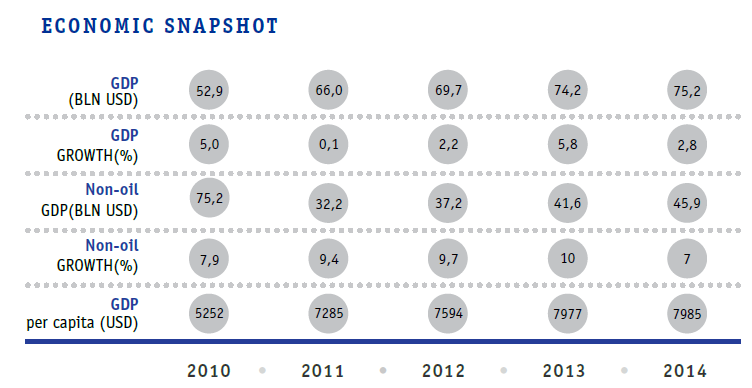
- In the past 10 years: GDP grew by 3 times, non-oil GDP by 2.5 times, GDP per capita by 2.6 times, strategic currency reserves by 29 times.
- Foreign debt of Azerbaijan is only 8.6% of the GDP, the volume of currency reserves accounts for about 68.4% of the GDP, and public deficit about 0.5% (2014).
- 38th most competitive economy among 148 countries and 1st among CIS members (WEF Global Competitiveness Report 2014-2015).
- Sovereign credit rating at investment level by three major international rating agencies: Standard and Poor’s, Fitch Ratings and Moody’s.
- Safety, government and political stability are considered the strongest factors by international business community operating in Azerbaijan (WEF Global Competitiveness Report 2014-2015).
Reformist business environment
- Top reformer of business regulations in the world according to the World Bank’s Doing Business 2009 and 2015.
- Low burden of government regulation.
- Strengthening welcoming business environment and legislative reforms are among the top priorities of “Azerbaijan 2020: the vision of the future” – national development concept.
Attractive investment climate
- NO restrictions to foreign investments. National regime applied.
- NO local content requirement.
- Party to all major multilateral instruments on protection and promotion of foreign investment.
- 47 bilateral investment treaties and 44 double taxation treaties with foreign countries.
- Third easiest among CIS countries and fully digitalised tax paying procedure.
- Over 450 e-services by state authorities.
Skilled labour force
- About half of the population is economically active. Total labour force reached 4.8 million persons.
- One of the highest employment rates in the region (95%).
- The main driver of employment is the private sector (74%).
- Extremely high literacy rate of 99.8%.
- Around 30 thousand students graduate from universities and other higher education institutions annually.
- Large number of Azerbaijani students studying in the best universities worldwide in the framework of the State Programme on Education of Azerbaijani Youth Abroad in 2007-2015.
- A large R&D center, the National Academy of Sciences with its 28 research institutes in parallel with 52 universities and 108 colleges ensures the scientific and HR component of economic development.
Strategic location
- Located on the south-eastern border of Europe serving as the natural bridge between Europe and Asia.
- Logistics hub for the Caspian region with the biggest airport, sea port and railway network.
- Easy access to the markets with over 600 million customers in CIS, Middle East and Central Asia.
- Outreach to 50 countries with almost 50% of world consumers within 4-hours-flight-range.
- Fast developing infrastructure
- The most state-of-the-art transport infrastructure in the region.
- About 19,000 km of hard-surface roads. Over 8 thousand km of roads built and re-constructed in the past 10 years.
- 6 international airports. Baku operates the biggest international airport in the region.
- Azerbaijan operates the biggest port on the Caspian Sea. A new port with capacity of 25 million tons cargo and 1 million containers a year is under construction. A new ship-building yard and the only one on the Caspian Sea commissioned in 2013.
- Over 2 thousand km of operational railroads. The so-called Iron Silk Way, Baku-Tbilisi-Kars trunk-railway
- is under construction. Once launched, it will connect European and Asian railway systems.
Abundant resources
- 9 climatic zones out of 11 existing in the world ranging from humid subtropical climate to semi-arctic.
- The territory of Azerbaijan stands out for its complex geological structure, diversity and manifold of minerals.
- Major deposits of oil and gas.
- Ferrous and nonferrous, rare and fine metals: iron and chromite ores, copper, lead and zinc, cobalt, molybdenum, aluminum, quicksilver, gold.
- Nonferrous minerals and construction materials: building stone, facing stone, clay, cement raw materials,
- construction stone, sand-gravel, sand, bituminous sands, perlite, pumice, gypsum, anhydride, alabaster, bentonite clays, sodium chloride, dolomite, quartzite, limestone for flux and soda, ceramic raw materials, mineral dye (clayey ochre), quartz sands, barite, pebble, brimstone, Icelandic spar, refractory and hard clays, natural soda flashes, zeolites.
Post Views: 20,841
Azerbaijan Azerbaijan economy 2016-01-31
Tags Azerbaijan Azerbaijan economy

 Oval Useful news from Azerbaijan and Caucasus
Oval Useful news from Azerbaijan and Caucasus


